If you’ve ever asked yourself, “What’s the difference between frequency, notes, and octaves?”—you’re not alone. These three terms get used together all the time, but they describe different aspects of sound. Understanding them will help you tune more accurately, make sense of music theory, and use digital pitch tools with confidence.
What Is Frequency?
- Definition: Frequency is the scientific measurement of sound waves—how many times the wave vibrates per second, measured in Hertz (Hz).
- Example: The pitch “A4” vibrates at 440 Hz, meaning the wave repeats 440 times every second.
Frequency is the raw number. It tells you the exact speed of vibration.
Try Our: frequency to note converter
What Is a Musical Note?
- Definition: A note is the musical name given to a specific frequency range.
- Western music uses 12 notes per octave (A, A#, B, C, etc.).
- Example: 440 Hz is labeled A4. If you sing at 442 Hz, you’re still on A4, just a few cents sharp.
Notes are how humans describe pitch in music, not just numbers.
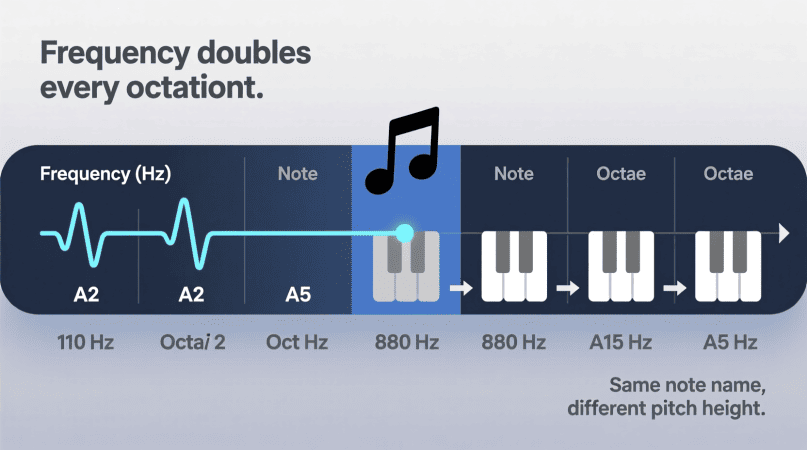
What Is an Octave?
- Definition: An octave is the relationship between two notes where one has double or half the frequency of the other.
- Example:
- A4 = 440 Hz
- A5 = 880 Hz (one octave higher)
- A3 = 220 Hz (one octave lower)
Octaves explain why musical patterns repeat higher and lower across the piano keyboard.
Quick Comparison Table
| Concept | What It Means | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Vibrations per second (Hz) | 440 Hz |
| Note | Musical label for a frequency | A4 |
| Octave | Doubling or halving of a frequency | A4 = 440 Hz → A5 = 880 Hz |
Why This Matters for Musicians
- Tuning instruments: Knowing that A4 = 440 Hz gives you a standard reference.
- Vocal training: Pitch tools often show note, frequency, and how many cents sharp/flat you are.
- Understanding harmony: Octaves explain why voices and instruments blend naturally across ranges.
Try Our: note to frequency converter
FAQs About Frequency, Notes, and Octaves
Q: What does frequency mean in music?
It’s the number of vibrations per second, measured in Hz.
Q: How do notes relate to frequency?
Notes are labels assigned to specific frequencies (e.g., A4 = 440 Hz).
Q: What is an octave?
An octave is when one note’s frequency is exactly double or half another’s.
Q: Why do notes repeat each octave?
Because doubling frequency preserves the same pitch “character,” just higher or lower.
Q: What’s the formula for calculating note frequencies?
f=440×2n/12f = 440 \times 2^{n/12}, where n is the number of semitones from A4.
Pitch Detector is a project by Ornella, blending audio engineering and web technology to deliver precise, real-time pitch detection through your browser. Designed for musicians, producers, and learners who want fast, accurate tuning without installing any software.
