Musicians, singers, and audio engineers often need to translate frequencies (Hz) into musical notes for tuning, analysis, or training. The Frequency → Note Converter makes this process simple and accurate with real-time results.
This tutorial walks you through the step-by-step process of converting frequencies to musical notes and understanding what the results mean.
Why Convert Frequency to Musical Notes?
- Tuning Instruments: Convert Hz readings into note names for tuning guitars, violins, and pianos.
- Vocal Training: Check what notes singers hit in real time or from recordings.
- Audio Analysis: Understand pitch stability in music production or speech analysis.
- Music Education: Teach students how pitch and frequency relate mathematically.
For recorded pitch analysis, try the Audio-File Pitch Detector.
Step-by-Step: Frequency → Note Conversion
Step 1: Open the Frequency → Note Converter
Visit Frequency → Note Converter on any device — no installation required.
Step 2: Input Frequency (Hz)
- Enter any value in Hertz (Hz) into the input box.
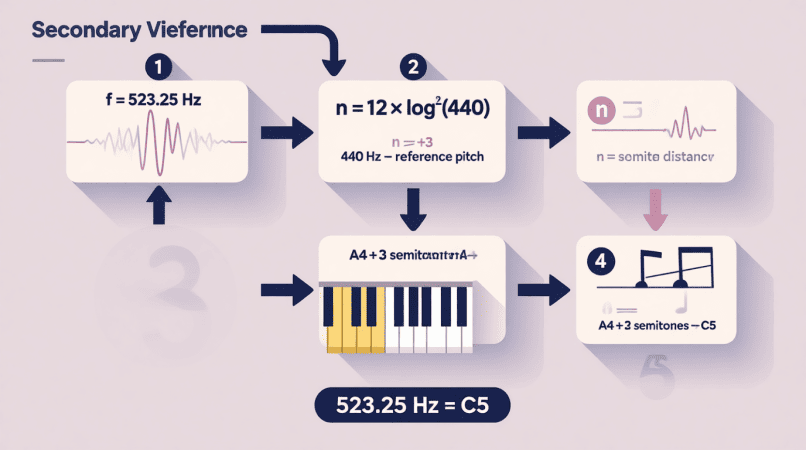
- Example: Type 440 Hz to find the note name and pitch accuracy.
Step 3: View Note Name & ±Cents Deviation
The tool displays:
- Note Name: e.g., A4 for 440 Hz.
- Octave Number: Determines register (e.g., A4 vs A3).
- ±Cents Deviation: Shows how sharp (+) or flat (−) the frequency is compared to the perfect pitch center.
Step 4: Adjust Tuning or Singing
- For instruments: Tighten or loosen strings to center the note.
- For singers: Practice holding notes until ±cents deviation is below 5¢.
See Breath Support & Pitch Accuracy for improving vocal stability.
Example Frequency → Note Table
| Frequency (Hz) | Musical Note | Octave | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| 440 Hz | A4 | 4 | Standard tuning reference |
| 261.63 Hz | C4 (Middle C) | 4 | Piano, vocal training |
| 329.63 Hz | E4 | 4 | Guitar string tuning |
| 196 Hz | G3 | 3 | Lower register instruments |
Tips for Accurate Results
- Quiet Environment: Background noise can interfere with readings.
- Proper Mic Placement: Keep 20–30 cm away from the source.
- Standard Tuning: Default is A4 = 440 Hz; orchestras often use A4 = 442 Hz.
Learn more about calibration in Accuracy & Calibration: Frequency → Note Conversion.
Common Applications
- Music Teachers: Demonstrate frequency-to-pitch relationships in lessons.
- Choirs: Check vocal harmonies for tuning consistency.
- Audio Engineers: Analyze recordings before pitch correction in DAWs.
FAQs
1. Does the tool work for live audio?
Yes, live input works with our Pitch Detector tool.
2. Can I analyze recordings?
Yes, use the Audio-File Pitch Detector for files.
3. How accurate is the conversion?
Within ±1 cent under optimal conditions.
Pitch Detector is a project by Ornella, blending audio engineering and web technology to deliver precise, real-time pitch detection through your browser. Designed for musicians, producers, and learners who want fast, accurate tuning without installing any software.
